
Lists the available realm flags that ksetup can detect.Īnalyzes the Kerberos configuration on the given computer.
Windows kinit command password#
Sets the password for the computer's domain account (or host principal).ĭeletes all information for the specified realm from the registry.Īllows you to specify a domain (if the hasn't already been set by the /domain parameter).Īllows you to use the kpasswd to change the logged on user's password.
Windows kinit command windows#
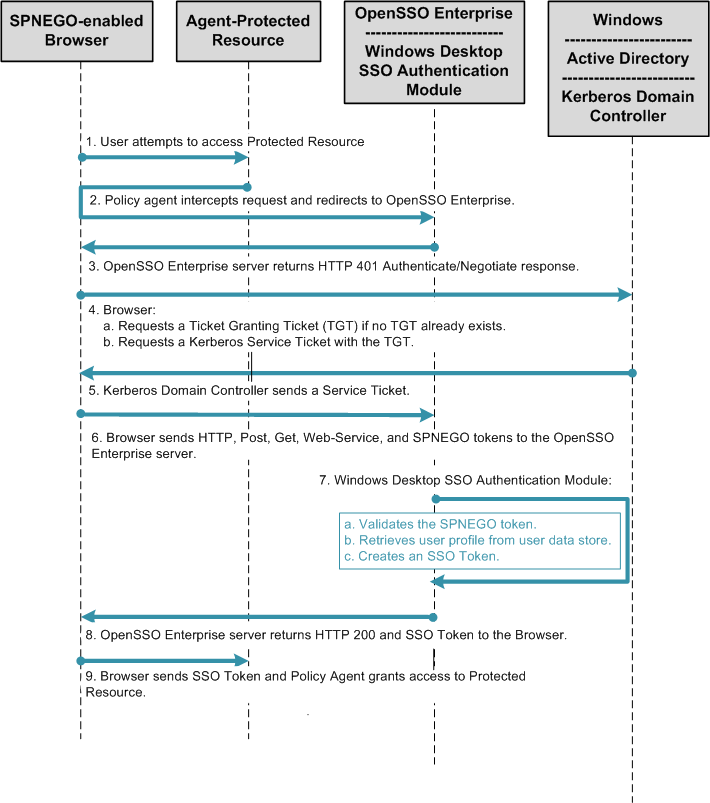
Makes this computer a member of a Kerberos realm.Īdds a kpasswd server address for a realm.ĭeletes a kpasswd server address for a realm.Īllows you to specify the name of a Windows computer on which to apply the changes. The Kerberos protocol can use DNS to locate KDCs by using only the realm name, but it must be specially configured to do so. Search the registry for the domain name of the user's realm and then resolves the name to an IP address by querying a DNS server. After configuration, the user of a client computer running the Windows operating system can log on to accounts in the Kerberos realm. Initialize registry keys that the Kerberos Security Support Provider (SSP) uses to locate a KDC for the Kerberos realm, if the computer is isn't a member of a Windows domain. These settings are used by workstations to locate Kerberos realms and by domain controllers to locate Kerberos realms for cross-realm trust relationships. You can use this tool to modify these settings. In Windows Server operating systems, it's kept in the registry. In non-Microsoft, Kerberos–based implementations, this information is usually kept in the nf file.

Specifically, this command is used to:Ĭhange the computer settings for locating Kerberos realms. Performs tasks related to setting up and maintaining Kerberos protocol and the Key Distribution Center (KDC) to support Kerberos realms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
